As we navigate through life, our bodies encounter various health challenges. These challenges can be broadly categorized as acute illnesses or chronic conditions. Understanding this distinction is crucial for recognizing symptoms, seeking appropriate treatment, and managing overall health, including what is an acute illness.
What is an Acute Illness?
An acute illness is a health condition that develops and lasts for a limited period, often a few days or weeks. Think of it like a sudden storm – it arrives quickly, disrupts your routine, but eventually passes. Common examples of acute illnesses include:
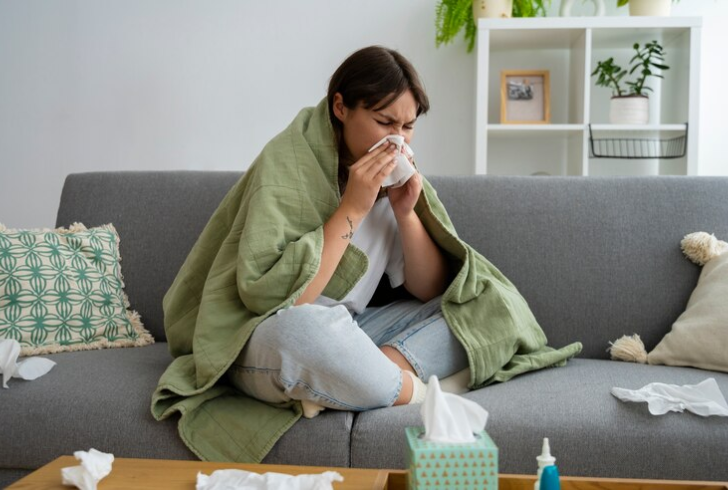

- The flu
- The common cold
- Bronchitis
- Strep throat
- Food poisoning
- Urinary tract infections (UTIs)
- Broken bones
- Burns
These illnesses often have well-defined symptoms, such as fever, cough, sore throat, nausea, or pain. Treatment for acute illnesses can involve medication, rest, and fluids to help your body fight off the infection or heal from the injury. In most cases, people recover completely from acute illnesses with proper care.
Chronic Conditions – A Different Story
In contrast to acute illnesses, chronic conditions develop and persist for an extended period, often months or even years. These conditions can’t be cured, but with proper management, their symptoms can be controlled and their impact minimized.
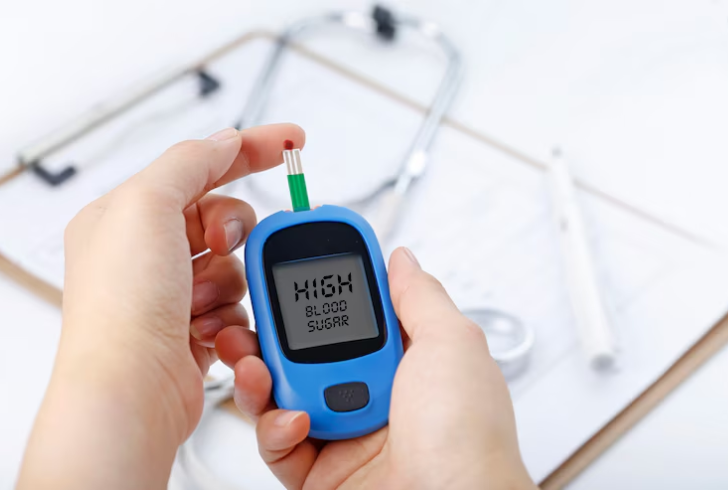
Some prevalent chronic conditions include:
- Diabetes
- Heart disease
- Arthritis
- Asthma
- High blood pressure
- Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)
The symptoms of chronic conditions can vary depending on the specific condition. They may be subtle at first or come and go in flare-ups. Effective management of chronic conditions often involves a combination of strategies, such as medication, lifestyle modifications (like diet and exercise), and physical or occupational therapy.
Causes of Acute and Chronic Conditions
Acute illnesses are triggered by:
- Viruses or bacteria enter the body, causing infections.
- Injuries sustained in falls, accidents, or overuse.
- Misuse of medications or drugs.
Chronic conditions often stem from a combination of factors, including:
- Unhealthy lifestyle habits like poor diet, physical inactivity, or smoking.
- Genetics – some people are more predisposed to certain chronic conditions due to their genetic makeup.
- Environmental factors like exposure to toxins or pollutants.
The Importance of Recognizing the Difference
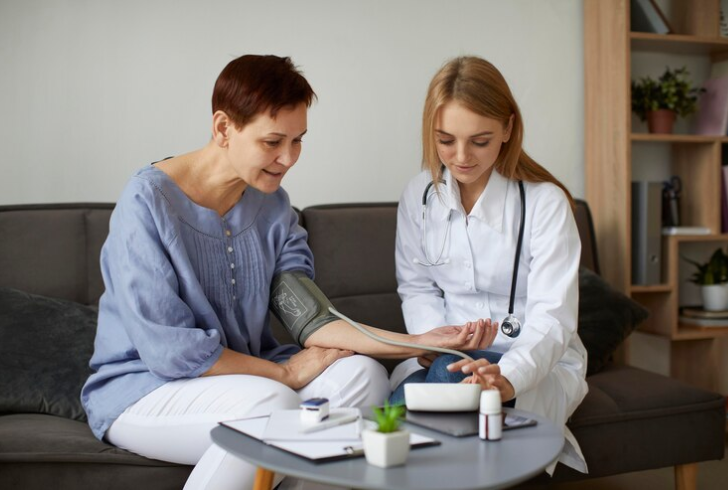

Distinguishing between acute and chronic illnesses is crucial for seeking appropriate care. Acute illnesses often need a visit to your doctor to receive a diagnosis and treatment plan. Early intervention can optimize recovery and minimize complications.
Chronic conditions, on the other hand, require ongoing management. Working with your doctor to develop a personalized management plan is essential for controlling symptoms and maintaining a good quality of life.
Living Well with Acute and Chronic Conditions
There’s a lot you can do to navigate both acute and chronic illnesses. Here are some tips:
Acute Illnesses:
- Practice good hygiene to prevent infections, a common cause of acute illnesses.
- Maintain a healthy lifestyle with a balanced diet and regular exercise to strengthen your immune system and promote well-being.
- Seek prompt medical attention when experiencing symptoms of an acute illness for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Chronic Conditions:
- Work with your doctor to develop a personalized management plan for your specific chronic condition.
- Adhere to your treatment plan, which may include medication, lifestyle modifications, or therapy.
- Maintain regular checkups with your doctor to track your condition and adjust your treatment plan as needed.
By understanding the distinctions between acute and chronic illnesses and taking proactive steps towards prevention and management, you can empower yourself to navigate health challenges effectively and live a fulfilling life.